Automation has become a key part of how modern businesses run today. Tasks that once required large teams are now handled by software solutions, but still many businesses rely on rule based systems that fail when data changes or decisions are unclear. Moreover, according to studies, it is depicted that about 70 percent of enterprises use automation today, but only a small number of them achieve full-scale results.
Robotic Process Automation helped businesses automate repetitive work and decrease manual effort. But RPA alone cannot think, learn or adapt. When processes involve unstructured data or unexpected scenarios, automation often stops and needs human help.
In this blog, we will explore how Agentic AI and RPA change that limitation. It explains how combining RPA with intelligent decision making creates the next phase of hyperautomation. We will also discuss how this approach and combination of Agentic AI with RPA development enables systems to act, learn and improve on their own while supporting real business growth.
What is Hyperautomation?
Hyperautomation is an enterprise automation approach that focuses on automating business processes and not just isolated tasks. It connects systems data and decision logic into a continuous automation flow. The objective is to decrease manual dependency. Moreover, according to Gartner, hyperautomation is one of the top 10 strategic technology trends and shows a shift from an option to a condition for survival.
Hyperautomation is enabled through a combination of technologies working together.
Key technologies enabling hyperautomation
- RPA executes repetitive and rule based actions across enterprise systems
- Artificial Intelligence supports reasoning and contextual knowledge
- Machine Learning improves decision quality through continuous learning cycles
- NLP allows automation to process emails, documents and conversational data
- Process Mining discovers process patterns and identifies optimization opportunities
Hyperautomation Vs Traditional automation
| Aspect | Traditional Automation | Hyperautomation |
| Automation Approach | Automates single tasks using fixed steps | Automates complete processes from start to end |
| Decision Making | Follows predefined rules only | Makes decisions using data and AI |
| Data Handling | Works mainly with structured data | Works with structured and unstructured data |
| Exception Handling | Stops and needs human help | Handles many exceptions on its own |
| Scalability | Difficult to scale across teams | Easily scales across systems and processes |
| Intelligence Level | Executes tasks without understanding | Understands context and learns over time |
| Maintenance Effort | Needs frequent manual updates | Needs fewer updates due to learning models |
| Process Optimization | Improvements are manual and slow | Continuously improves using data insights |
| Business Impact | Saves time and reduces basic costs | Improves agility, efficiency and decision quality |
The Role of RPA in Today’s Business Landscape
Robotic Process Automation plays an important role in automating enterprise solutions. It allows organizations to automate high-volume recurring tasks by working in the same way as human actions across applications & RPA is highly adopted because it is fast to deploy, works with existing systems and delivers fast efficiency gains.
RPA operates through a structured architecture that separates execution control and system integration.
RPA architecture
- Robots or bots
- Attended bots support users triggering actions during human interaction
- Unattended bots run independently and execute tasks without human involvement
- Centralized management console
- Helps control bot deployment scheduling and workload distribution
- Monitors performance failures and execution logs
- Integration with IT infrastructure
- APIs for direct system communication
- Databases for reading and writing structured data
- Desktop automation for legacy systems
- Web scraping for extracting data from web interfaces
This architecture makes RPA reliable for structured and rule driven workflows.
Limitations of Traditional RPA
While RPA development is effective for execution, it has clear limitations in complex business environments. Traditional RPA depends on fixed logic and predefined rules, which restricts its ability to handle variability.
Key RPA challenges
- No cognitive capability to understand context or unstructured data like emails, documents or images
- High maintenance effort when user interfaces or business rules change
- Limited scalability when processes involve frequent exceptions
- Bots often stop execution when unexpected inputs appear
Also, modern enterprises operate in data rich and constantly changing environments. Processes now require interpretation and learning over time. RPA helps at execution but lacks intelligence. This creates a gap that can only be filled by combining RPA with AI technologies to support next-generation automation.
Also Read: Robotic Process Automation Use Cases In Various Industries
Understanding Agentic AI Role in Hyperautomation
Agentic AI refers to AI systems designed to act as autonomous agents and not just passive tools. These systems can perceive their environment, assess multiple options and take actions to achieve defined results. Unlike traditional AI models that respond only to inputs, Agentic AI systems operate continuously and adjust their behavior based on outcomes.
Agentic AI is built for autonomy and decision-making. It can learn from experience, adapt tasks dynamically and operate with very little human intervention. This makes it best for complex environments where rules cannot cover every scenario.
Core building blocks of Agentic AI
- Reinforcement learning enables agents to learn optimal actions through feedback and rewards
- Generative AI models help with reasoning and content generation
- Neural networks process high volumes of structured and unstructured data
Key Features of Agentic AI
Agentic AI systems are designed to evolve over time. Their intelligence improves as they process more data and encounter new situations.
Adaptive Learning
- Uses historical and real time data to refine decision models
- Adjusts behavior based on outcomes rather than fixed rules
Autonomous Decision Making
- Decision engines evaluate context constraints and goals
- Agents select actions using policy based and probabilistic models
- Feedback loops continuously improve decision quality
Scalability and Flexibility
- AI agents scale in workflows without manual rule expansion
- Systems adapt to fresh data sources and changing business needs
- Distributed agents operate independently while aligning with global objectives
The Impact of Combining RPA and Agentic AI for Hyperautomation
When RPA and Agentic AI work together, automation moves beyond task execution into intelligent process control. RPA continues to perform high speed repetitive actions while Agentic AI takes responsibility for decision, context evaluation and exception handling. This combination creates systems that can operate with minimal human input.
In this stage, automation is not just triggered by rules. Decisions are taken by data patterns, business goals and real time signals. As processes evolve, the system adapts without constant reconfiguration.
Integration architecture
A hyperautomation architecture connects execution intelligence and data layers into a unified flow.
- RPA layer
Executes structured tasks such as data entry validation and system updates - Agentic AI layer
Interprets context, evaluates options and decides the next best action - NLP layer
Processes emails, documents, chat messages and user requests - OCR layer
Extracts data from scanned files, invoices, forms and images - Machine learning layer
Continuously improves decision quality and process efficiency
These components communicate through APIs and event driven triggers to guarantee smooth execution and intelligence.
For Instance:
Consider an automated invoice processing system that requires hyperautomation.
- OCR extracts data from incoming invoices
- NLP reads email content and identifies intent or priority
- Agentic AI validates the invoice, evaluates risk and decides the approval path
- RPA enters data into ERP systems and triggers payments
- ML models analyze outcomes and improve fraud detection and routing logic
Over time, the system becomes faster, more accurate and less dependent on manual review. This shows how combining RPA with Agentic AI enables true hyperautomation that can scale and adapt to real business conditions.
Process for Implementing RPA and Agentic AI to Enable Hyperautomation
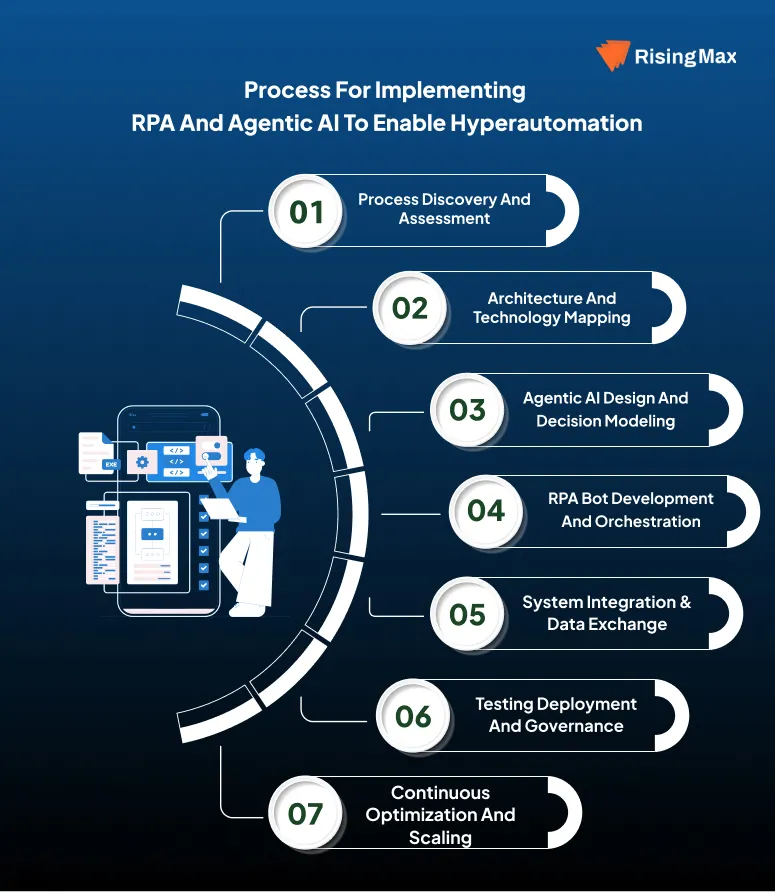
Building a system that combines RPA and Agentic AI requires designing an automation architecture where execution intelligence and data flow work together.
Process Discovery and Assessment
The first step is knowing how existing business processes operate in working environments. Workflow systems and data flows are analyzed to find repetitive actions, decision points and exception scenarios. This helps define where RPA delivers value and where agentic intelligence is required.
Architecture and Technology Mapping
Next, a modular architecture is designed to clearly separate execution and intelligence layers. RPA handles task execution while Agentic AI manages reasoning and decisions. NLP, OCR and ML components are mapped to specific process needs to ensure performance scalability and security.
Agentic AI Design and Decision Modeling
Agentic AI components are built to set priorities and select actions. Decision models are trained using historical and real time data. Feedback mechanisms allow agents to learn from outcomes and adapt to changing business conditions.
RPA Bot Development and Orchestration
Following design modelling, attended and unattended bots are developed to execute tasks across enterprise systems. Bots are triggered by AI driven decisions rather than static rules. Orchestration ensures proper sequencing and workload distribution.
System Integration & Data Exchange
APIs, event-driven workflows and databases connect enterprise systems and automation platforms. This allows data exchange between agents and bots while maintaining consistency.
Testing Deployment and Governance
Automation workflows are validated for performance and exception handling. Governance frameworks guarantee compliance and controlled decision making. Monitoring dashboards provide better visibility into both RPA bot actions and AI decisions.
Continuous Optimization and Scaling
In this stage, ML models and agent policies are constantly improved using live operational data. The system changes without frequent redesign and scales in new processes and data sources.
To implement such advanced automation reliably, organizations partner with an experienced AI development company that can design, integrate and support RPA and Agentic AI systems at scale.
How RPA and Agentic AI Deliver Hyperautomation Across Industries

Banking and Finance
Financial operations demand speed with strict control. Automation in this environment should process large transaction volumes while responding instantly to risk signals. Execution systems handle posting and reconciliation, while intelligence continuously evaluates transaction behavior and compliance exposure.
- Transaction flows are adjusted dynamically based on risk scoring
- Approval paths change automatically as customer behavior evolves
- Settlement and compliance actions are triggered without manual rule updates
This creates an automated financial operation that adapts rather than based on static rules.
Also Read: Use Cases Of Robotic Process Automation In Banking
Healthcare
Healthcare workflows balance administrative efficiency with clinical urgency. Hyperautomation helps in this by executing structured tasks while intelligence evaluates patient risk and operational load.
- Patient records and claims are updated across systems without manual effort
- Case prioritization changes as new clinical data becomes available
- Follow ups and escalations are routed automatically based on urgency
Automation adapts to patient volume and risk levels, allowing care teams to focus on decision making rather than coordination.
Retail
Retail environments change rapidly due to demand shifts and customer behavior. Automation here focuses on responding to these signals in near real time.
- Inventory levels are adjusted based on sales velocity and demand patterns
- Pricing and promotions respond to market conditions automatically
- Customer interactions trigger backend actions without manual handling
This allows retail operations to stay aligned with demand without constant human intervention.
Manufacturing
Hyperautomation in the manufacturing industry helps with operational continuity and efficiency. Systems execute production and procurement tasks while intelligence monitors performance and supply risks.
- Production plans adjust when machine performance degrades
- Maintenance is triggered before failures can happen
- Supplier orders change dynamically based on production needs
Operations remain stable and responsive even as conditions change.
Logistics and Supply Chain
Logistics requires constant coordination across time and geography. Automation manages execution while intelligence adapts to external conditions.
- Shipment routes change based on real time constraints
- Delivery priorities shift as conditions evolve
- Documentation and billing remain synchronized automatically
This enables supply chain operations to respond to disruption without manual rework.
Key Business Benefits of Hyperautomation Using RPA and Agentic AI
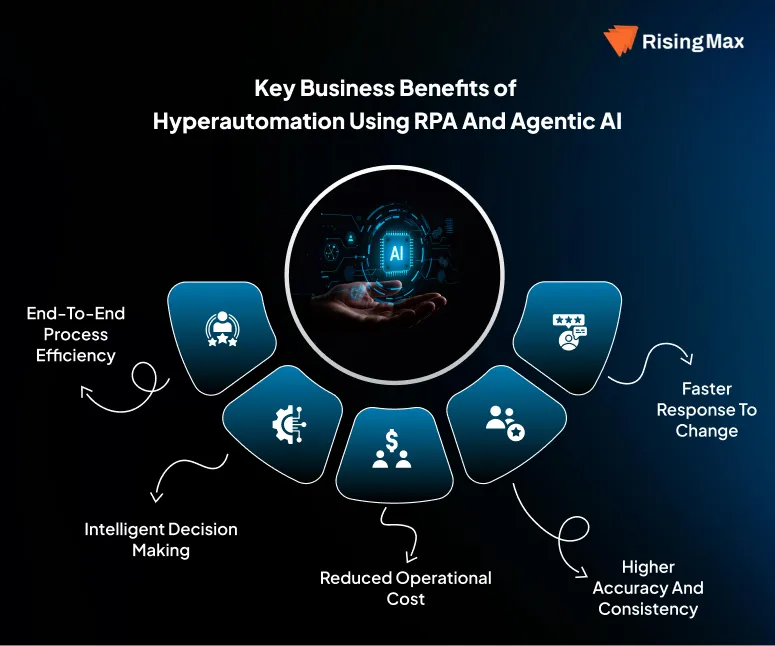
Hyperautomation delivers value by combining fast execution with intelligent decision making. When RPA and Agentic AI work together, automation moves beyond task efficiency and begins to improve how entire processes operate.
End-to-End Process Efficiency
Hyperautomation removes manual tasks and automates all the processes in systems and departments. Decisions and execution happen within the same automated flow which reduces delays and cycle times across complex workflows.
Intelligent Decision Making
Unlike rule based automation, hyperautomation adapts to changing inputs. Agentic AI evaluates context data and outcomes to guide execution, which improves decision quality over time.
Reduced Operational Cost
Automated decision control lowers the need for manual rework and exception handling. This leads to lower processing costs and more efficient use of human resources.
Higher Accuracy and Consistency
RPA executes tasks with precision while AI reduces errors caused by inconsistent decision logic. Processes remain consistent even at high volumes.
Faster Response to Change
Business rules, market conditions and customer behavior change frequently. Hyperautomation adjusts execution paths automatically rather than waiting for rule updates.
Common Pitfalls in Hyperautomation and How to Avoid Them
Hyperautomation delivers value only when execution and intelligence are applied in the appropriate manner. Many businesses face issues in implementing hyperautomation, not because the technology fails, but because of how it is applied.
Automating Broken Processes
Hyperautomation should improve how work flows and not just simply speed it up. When inefficient or unclear processes are automated, errors increase faster and become harder to control.
For example, a business might automate its approval workflow without redefining ownership or decision criteria. As volumes increase, approvals are executed automatically, but incorrect decisions rise because the process logic itself is flawed.
Treating AI as a Rule Engine
Agentic AI is designed to learn from data and possible results. When it is forced to work like a static rules engine, its ability to adapt is usually lost.
For example, this happens when fraud detection models are locked to fixed thresholds. As transaction patterns change, the system continues making outdated decisions, which leads to increased false positives and customer friction.
Poor Data Quality
Hyperautomation works on accurate and timely data to make decisions. If the provided data is inconsistent or incomplete, the quality of automation results quickly degrades.
For instance, when customer data is spread across disconnected systems. The AI agent receives conflicting inputs and gives unreliable decisions, which then will need frequent manual intervention.
Lack of Governance
As automation becomes more autonomous, control and accountability become highly important. Without governance, it becomes really challenging to know why a system made a specific decision.
For instance, an automated financial process executes payments based on AI recommendations without defined approval. When a discrepancy occurs, teams cannot trace the decision path, creating compliance and audit risks.
Scaling Too Early
Hyperautomation systems need time to stabilize and learn. Expanding automation before decision models are mature often leads to widespread issues.
For example, this is seen when a pilot automation performs well in one department and is immediately rolled out in the enterprise. As data patterns vary across teams, decision accuracy drops and automation should be paused for rework, delaying value realization.
The Future of Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation is moving toward systems that do not wait for instructions but act based on predicted needs. As decision models and automation will shift from reactive execution to proactive process control. RPA will continue to handle execution at scale and Agentic AI will evolve to manage long-term goals and multi-step reasoning across workflows.
Advanced Cognitive Capabilities
Future hyperautomation systems will use predictive intelligence to anticipate events before they occur. Agents will identify early signals such as demand changes, risk patterns or operational delays and adjust execution paths automatically. This reduces disruption and enables continuous optimization.
Quantum Computing Impact
Quantum computing has the potential to speed up complex decision calculations that are currently resource intensive. In hyperautomation, this means faster optimization of large scale workflows, better simulation of outcomes and improved decision accuracy in high-complexity environments such as finance and manufacturing.
Edge AI and distributed processing
As real-time automation becomes critical, processing will move closer to the data source. Edge AI enables decisions to be made locally on devices or edge systems without being based on centralized infrastructure. This supports faster response and scalable automation in environments.
Conclusion
Hyperautomation focuses on creating systems that can execute, decide and adapt as business conditions change. As workflows become more data-driven and complex, rule based automation alone cannot deliver consistent outcomes, which businesses are looking for today.
By combining RPA with Agentic AI, businesses move from basic automation toward intelligent process control. RPA provides reliable execution at scale, while Agentic AI adds learning, context awareness and autonomous decision-making. Together, they enable automation that can handle exceptions, evolve with data and operate with minimal human involvement.
To implement and scale such systems effectively, many organizations choose to partner with an experienced AI development company like RisingMax because with the right architecture, governance and technical expertise, businesses can unlock the complete potential of hyperautomation.
FAQs
1. What is hyperautomation in simple terms?
Hyperautomation is the use of multiple technologies such as RPA, AI, and machine learning to automate entire business processes, including decision-making, rather than just individual tasks.
2. What role does Agentic AI play in hyperautomation?
Agentic AI acts as the decision-making layer. It evaluates context, learns from outcomes, and guides RPA bots on what actions to take and when.
3. Can hyperautomation work without Agentic AI?
Hyperautomation can exist at a basic level without Agentic AI, but it remains limited. Without autonomous decision-making, automation struggles to adapt to complex and changing scenarios.
4. Which business processes are best suited for hyperautomation?
The business processes that are best-suited for hyperautomation are those with high volume, frequent exceptions, and decision dependency, such as finance operations, customer onboarding, claims processing, and supply chain management.
5. How much does it cost to implement hyperautomation?
The cost to implement hyperautomation ranges between $8,000 to $35,000, depending on process complexity, data readiness and autonomy level. Small pilot projects may need a moderate investment, while enterprise-wide hyperautomation needs higher upfront costs but delivers long-term operational savings.
6. How long does it take to implement hyperautomation?
Implementation timelines vary. A pilot can take a few weeks, while large-scale deployments may take several months, depending on integration and decision complexity.
7. Is hyperautomation more expensive than traditional automation?
Yes, in the beginning, but hyperautomation reduces long-term costs by minimizing manual intervention, rework, and exception handling compared to rule-based automation.
8. What industries benefit the most from hyperautomation?
Industries that benefit the most from hyperautomation are:
- Banking
- Healthcare
- Retail
- Manufacturing
- Logistics
9. How does hyperautomation handle unstructured data?
Hyperautomation uses technologies like NLP and OCR to process emails, documents, and scanned files, enabling automation beyond structured data sources.
10. What are the biggest risks in hyperautomation projects?
Common risks in hyperautomation integration projects include:
- Poor data quality
- Lack of governance
- Automating inefficient processes
- Scaling automation too early.
11. How is governance managed in hyperautomation systems?
Governance is handled through decision audit logs, approval thresholds, access control, and monitoring dashboards to ensure transparency and compliance.
12. Can humans stay involved in hyperautomation workflows?
Yes. Human-in-the-loop models allow humans to review or approve critical decisions while routine actions remain fully automated.
13. How do businesses measure the success of hyperautomation?
Success is measured using metrics such as process cycle time reduction, exception handling rate, decision accuracy, cost savings, and scalability.
14. Why should businesses partner with an AI development company for hyperautomation?
Hyperautomation requires advanced system design, AI decision modeling, and deep integration expertise. Partnering with an experienced AI development company like RisingMax helps ensure secure, scalable, and high-performing hyperautomation solutions.














