The enterprise world is currently witnessing a massive influx of capital into artificial intelligence, with the global AI market projected to reach $1.85 trillion by 2030. The constant advancements of AI have led 78% of global businesses to adopt AI into their operations. However, this rapid adoption also presents a paradox –
“While organizations are eager to deploy Large Language Models (LLMs), 77% of companies remain deeply concerned about AI hallucinations.”
These “hallucinations,” in which a model generates information that is factually incorrect or fabricated information, represent a fundamental bottleneck to integrating AI in data-critical tasks.
General Understanding of AI Hallucinations
In basic terms, to understand why the current version of LLMs poses a hallucination hurdle, it is important to examine how these modules function.
Scientifically, LLMs do not “understand” content or verify facts; they operate through probabilistic generation, predicting the most likely next word based on statistical correlations learned during training. This lack of a built-in feedback loop or internal fact-checking mechanism means an LLM will often output false information with high confidence because it lacks awareness of its own uncertainty.
In high-stakes fields like legal or medical services, these guesses are catastrophic, with some studies showing hallucination rates as high as 69% to 88% when models are tasked with specific legal queries.
Proposed Thesis of The Synergy of RAG and MCP
Building the foundation of trust requires a robust, two-pronged technical approach.
First, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) acts as the engine of factual grounding, infusing LLMs with up-to-date, AI-ready data from a company’s own internal sources to anchor responses in reality.
Second, the Model Context Protocol (MCP) provides the secure, standardized data infrastructure needed to bridge the gap between these powerful models and complex enterprise data silos.
Together, RAG and MCP complement each other. MCP functions as the governed data-access layer (think of it as a “librarian and security guard”), while RAG leverages that layer to retrieve the precise context needed at query time to eliminate hallucinations and secure the enterprise AI stack.
Now that you have an overview and basic understanding of AI hallucinations and how RAG – MCP can help resolve these deviations. Let us evaluate each aspect one by one, including the business outcomes and industry-related use cases of RAG and MCP.
Why LLMs Hallucinate in Generating Answers

At a fundamental level, Large Language Models (LLMs) are not truth-seeking engines; they are sophisticated pattern-recognition systems. Scientifically, LLMs function through probabilistic generation, predicting the most likely next word based on statistical correlations learned from vast training datasets.
They do not possess a built-in mechanism for internal fact-checking or a genuine “understanding” of the content they produce.
Instead, when a model encounters a knowledge gap, it fills that space with the most statistically probable completion, often leading to confident but entirely fabricated outputs. This lack of an internal feedback loop means that any error in initial reasoning can propagate into a full-blown hallucination, which the model presents with the same fluency as a verified fact.
Why Public AI Models Fail the Enterprise
One of the most significant entrepreneurial risks stems from the static nature of LLM training. Publicly available models rely on static and often outdated training data, which lacks the real-time, proprietary context required for business operations.
Consequently, when tasked with queries regarding internal company policies, niche technical troubleshooting, or real-time customer data, these models default to their general training set, which is frequently irrelevant or simply wrong for the specific enterprise context.
The stakes of this knowledge gap are high:
- 77% of companies cite hallucinations as a primary concern blocking AI adoption.
- In specialized fields like legal services, state-of-the-art models have shown hallucination rates ranging from 69% to 88% when responding to specific queries.
Why Even Standard Retrieval Isn’t Enough? (The Need of MCP)
While Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) was designed to ground LLMs in external evidence, standard RAG implementations are not a “silver bullet” for eliminating hallucinations.
“Terminology Usage – What does grounding results in LLM mean?
Grounded results simply mean producing answers that are factually correct and involve less guesswork; they rely on credible sources of information.
Conventional RAG typically relies only on unstructured, general data, which introduces several residual risks:
- Data Quality and Noise: If the internal knowledge base contains errors, biases, or redundant information, the LLM will reflect those flaws in its responses.
- Contextual Blind Spots: RAG systems may fail to grasp the nuances of user intent, leading the model to miss key points or incorporate irrelevant context.
- Operational Failures: For instance, a cellular operator’s RAG chatbot might provide a subscriber with an incorrect bill amount because the retrieved unstructured data included charges that weren’t theirs.
Ultimately, standard RAG remains limited by its focus on factual grounding without addressing the internal reasoning flaws of the LLM itself. To eliminate such differences, enterprises are now looking to shift towards more advanced frameworks such as.
Also Read | How Agentic AI in Clinical Workflow Can Solve $1 Trillion Coordination Burden
Understanding RAG: How To Get More Grounded Results from LLMs?
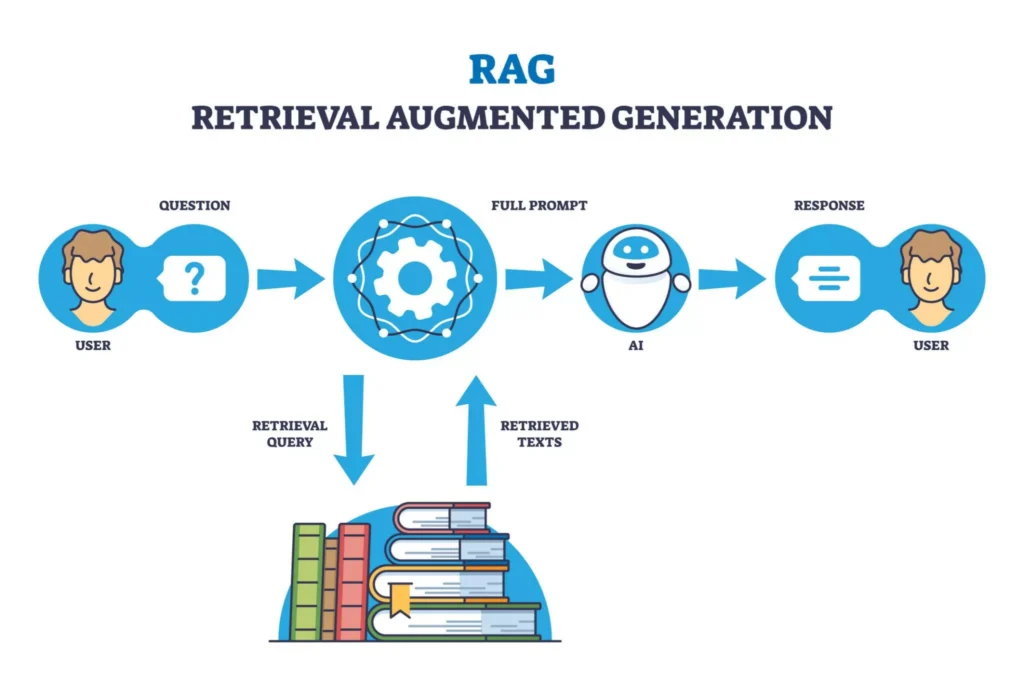
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a powerful tool designed to enhance Large Language Models (LLMs) by incorporating external evidence retrieved at inference time into their outputs. This approach moves AI away from reliance on static, parametric knowledge toward a non-parametric, i.e., dynamic retrieval module that can access a dynamic evidence corpus.
The standard RAG workflow operates through three distinct scientific modules:
- Query Encoder: This module processes the user’s natural language input into a mathematical representation or “query representation”.
- Retriever: Using the encoded query, the retriever fetches a ranked list of relevant documents from an external corpus (data source), such as a database, API, or document store.
- Generator: The generator then synthesizes a final response by conditioning its generation on both the original user query and the retrieved factual context.
GenAI Data Fusion: Beyond Unstructured Retrieval to “RAG+”
While conventional RAG often grounds models using only unstructured data (like PDFs or wikis), this can still lead to RAG hallucinations if the retrieved text is noisy or irrelevant. The next step towards achieving more optimized results is GenAI Data Fusion, which infuses LLMs with a combination of structured data (from CRM or DBMS systems) and unstructured data.
This data-as-a-product approach enables AI to access the structured data for a single business entity, such as a specific customer, vendor, or order, in real time. By unifying data from fragmented silos like SAP or Salesforce and delivering it at conversational latency, GenAI Data Fusion transforms RAG into a more precise RAG+ framework.
Research indicates that integrating structured knowledge graphs into this dual-pathway approach can reduce hallucinations by up to 18% in specialized domains like biomedical QA.
Benchmarking The Factual Integrity of RAG Systems
To make AI a production-ready tool, organizations must utilize rigorous evaluation metrics.
The sources highlight several key performance indicators used to verify the factual integrity of RAG systems:
- Trigger Exact Match (EM): This metric quantifies whether the generated output is factually correct or not.
- Recall@K: Used specifically to evaluate the retriever’s (one who imports information from external sources) effectiveness, this measures whether the necessary factual context is included within the top K (e.g., top 10 or 15) retrieved results.
- FactScore: A high-resolution metric used to evaluate fine-grained atomic factual precision, ensuring every claim made by the AI is backed by retrieved evidence.
By applying these metrics, developers can achieve what the “Agentic Maturity Model” describes as Safe Agentic Orchestration, where AI systems are trustworthy enough to handle multi-step tasks autonomously.
Role of MCP: From Fragmented Information to Unified Output
Historically, integrating a Large Language Model (LLM) with external databases or APIs required time-consuming custom engineering for every new service. MCP (Model Context Protocol) solves this by providing a universal standard that allows AI agents to seamlessly “plug into” any data source or tool without custom coding for each new integration.
By decoupling AI models from specific APIs, MCP enables servers to declare their capabilities, such as tools, data, and prompts, in a machine-readable way. This standardization ensures that AI assistants are no longer isolated but become context-aware participants in the enterprise ecosystem, capable of maintaining consistent context as they move between disparate datasets.
How MCP Governs Data with Precision?
MCP operates as a sophisticated intermediary between the LLM and sensitive enterprise data, fulfilling two critical roles: accurate retrieval and governance.
Retrieval and Validation: In this role, MCP uses Agentic Retrieval to intelligently analyze user intent and search across connected sources, including CRMs, ERPs, and internal wikis, to extract specific facts rather than just raw documents.
The Context Validation and Structuring component then scrutinizes this data for accuracy and recency before formatting it into a concise, rich prompt that the LLM can optimally process, which is essential for minimizing hallucinations.
Governance and Compliance: Simultaneously, MCP acts as a vigilant protector through Security Enforcers. It applies granular Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), ensuring that an LLM only accesses data that the specific user is authorized to see. Furthermore, it employs sophisticated data masking and anonymization to protect sensitive values, such as PII or financial figures, while retaining the context necessary for the LLM to function.
Understanding the Architecture of MCP (Model Context Protocol)
MCP follows a robust client-server architecture designed to handle the complexity of multi-source enterprise environments. This framework is composed of three primary pillars:
- MCP Host: The central AI application or agent runtime (e.g., Claude Desktop or a custom Python agent) that coordinates multiple clients to aggregate context from various origins.
- MCP Client: A module within the host that maintains a dedicated one-to-one connection with a specific server, managing the channel and fetching context as needed.
- MCP Server: An independent program that exposes specific tools and data (such as GitHub, Slack, or local files) to the client.
In technical terms, the system utilizes a JSON-RPC data layer for lifecycle management and capability discovery, and a versatile transport layer that supports both local STDIO pipes and remote HTTP/SSE connections with authentication. This modularity allows an enterprise to scale its AI initiatives across numerous use cases without the operational nightmare of managing custom point-to-point integrations.
Till now, we have understood the varying and dedicated roles of RAG and MCP. But if we combine these two, then the chances are that the LLM will give more grounded and unified output. The following section covers the mechanics of integrating RAG and MCP to reduce AI hallucinations.
How MCP Enhances RAG To Reduce AI Hallucinations
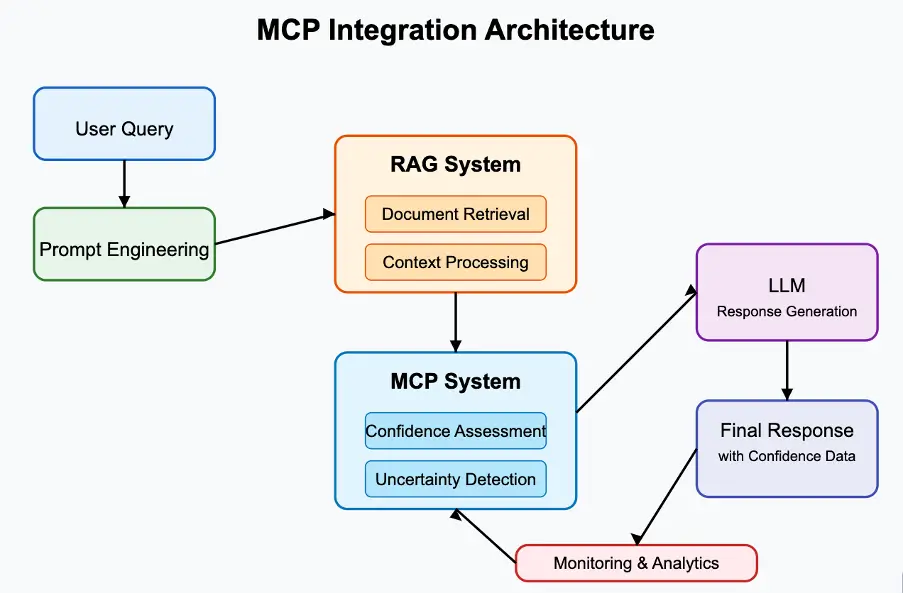
While RAG is a specific technique focused on improving output quality through retrieved information, MCP provides the broader, governed framework for all AI-data interactions.
By implementing RAG on top of an MCP-based architecture, enterprises ensure that the data retrieved for grounding is drawn only from authorized and verified sources. This creates a secure informational sandbox where the LLM can operate with maximum utility without risking access to restricted or predicted information.
One of the most significant entrepreneurial hurdles in scaling AI is the challenge of connecting LLMs across various enterprise silos. Traditionally, every new data source required a custom-coded integration, making systems difficult to maintain and scale.
MCP simplifies this process by replacing fragmented point-to-point connectors with a unified, open standard. This standardization offers several business benefits, such as
- Reduced Development Time: Developers build against one standard protocol rather than dozens of ad-hoc APIs.
- Plug-and-Play Scalability: New capabilities, such as a SQL database or a Slack server, can be “plugged in” without rewriting the core RAG pipeline. Such plug-and-play functionality can also be achieved with the help of Self-RAG and REPLUG frameworks.
- Operational Efficiency: Centralizing context management through MCP prevents the snowflake problem, where every AI application requires bespoke tuning and maintenance.
Deploying Response Validators and Guardrails
Even with precise RAG grounding, the probabilistic nature of LLMs means a residual risk of hallucination remains. The MCP duo addresses this by implementing Response Validators and Guardrails.
After the LLM generates a response, the MCP layer intercepts the output before it reaches the end-user to scrutinize it for several factors:
- Does the response align perfectly with the factual context retrieved by the RAG module?
- Does the output adhere to predefined enterprise policies and legal standards (e.g., “Do not disclose specific account balances”)?
- Does it avoid generating biased, harmful, or inappropriate content?
If a response fails these checks, the MCP layer can modify the response, flag it for human review, or prevent its delivery entirely. This provides a crucial automated verification step, ensuring that the final output is not only fluent but also factually sound and compliant with corporate governance requirements.
Accelerating Deployment with MCP via No-Code Modularity
The biggest challenge in enterprise AI adoption is not the AI model itself. It is the difficulty of managing different data sources, strict security rules, and custom workflows across hundreds or even thousands of AI agents. This creates a serious operational bottleneck for organizations.
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) solves this problem by offering a modular, no-code framework for agent enablement. MCP hides the complexity of data integration and context management behind standardized components. Because of this abstraction, business analysts and domain experts can build, configure, and deploy AI agents using easy-to-use templates.
This modular design also speeds up time-to-market. Instead of creating fragile, custom connectors for every new database or API, teams can use pre-built connectors to connect large language models (LLMs) with existing enterprise systems. In real-world deployments, this approach has greatly reduced custom integration work, helping organizations deliver AI solutions faster and unlock business value sooner.
Ensuring Out-of-the-Box Regulatory Compliance for Enterprise Use
For enterprises in regulated sectors like banking, healthcare, and defense, security concerns are often the final blocker to AI deployment. MCP functions as a sophisticated “security guard” that builds compliance directly into the protocol level.
- Healthcare (HIPAA): MCP’s Security Enforcers apply stringent, HIPAA-compliant data masking and anonymization techniques, ensuring that no Protected Health Information (PHI) is exposed to the LLM during processing.
- Financial Services: The protocol uses Response Validators to monitor AI outputs in real-time, ensuring they adhere to industry regulations (e.g., PCI DSS, fair lending practices) and legal guidelines before reaching the end-user.
- Global Privacy (GDPR/CCPA): Through granular Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), MCP ensures an AI agent only accesses data that the specific user is authorized to see, maintaining strict data boundaries and preventing unauthorized exposure of PII.
Multi-Industry Use Cases: RAG and MCP in Action
By transforming Large Language Models (LLMs) from isolated predictors into context-aware assistants, enterprises are realizing significant operational efficiencies.
RAG-MCP Use Cases in Financial Services
In the highly regulated financial sector, trust is the primary currency. Organizations are utilizing RAG and MCP to bridge the gap between complex internal data, such as customer profiles, loan agreements, and shifting policy documents, and front-line service.
- The Technical Workflow: MCP’s Secure Data Connectors provide authenticated pathways to sensitive account details and internal policy databases. When a representative queries a model regarding mortgage eligibility or investment nuances, the Agentic Retrieval component pulls specific, real-time clauses instead of generalized snippets.
- Governance and Safety: Critical to this process are Security Enforcers that redact PII (Personally Identifiable Information) before data reaches the model, and Response Validators that ensure suggested answers adhere to fair lending practices and disclosure requirements.
- Business Impact: This architecture reduces response times and human error while providing a robust audit trail for compliance teams.
RAG-MCP Use Cases in Healthcare
The healthcare industry faces a “data paradox”: the need for rapid access to the latest clinical research versus the absolute mandate of patient privacy.
Secure Factual Grounding: MCP enables researchers and physicians to query vast electronic health records (EHRs) and medical journals again through a secure “informational sandbox”.
Technical Safeguards: The protocol applies stringent HIPAA-compliant data masking and anonymization, allowing the AI to process the context of a patient’s journey without ever seeing sensitive values like Protected Health Information (PHI).
Scientific Outcomes: In biomedical QA tasks, research indicates that integrating structured knowledge graphs with RAG through these governed pathways can reduce hallucinations by up to 18%.
RAG-MCP Use Cases in Manufacturing
For manufacturing, downtime is a multi-million dollar problem. Frontline technicians often struggle to find specific troubleshooting steps within voluminous technical manuals.
- Real-Time Troubleshooting: RAG and MCP link directly to digital schematics, maintenance logs, and safety protocols. When a machine error occurs, the system pinpoints the exact section of a manual related to the specific error code, presenting the information clearly through Context Validation.
- The Safety Guardrail: A crucial, technically sound feature is the use of Response Validators to ensure any AI-generated advice adheres strictly to certified operational procedures, preventing potentially dangerous hallucinated safety instructions.
- Operational Gains: Deployments have shown significant improvements, such as a 28.6% reduction in resolution time for complex technical queries.
Conclusion
AI hallucinations are a major barrier to enterprise adoption. They happen because large language models (LLMs) work on probability, not real-time facts. Without a strong grounding in trusted data, models can produce confident but incorrect answers. Fixing this billion-dollar accuracy problem requires combining Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with the Model Context Protocol (MCP).
RAG improves accuracy by grounding model responses in verified, proprietary enterprise data. MCP adds the missing foundation by providing a standardized and secure infrastructure. In this way, the RAG ensures fetching the right context at the right time while MCP enforces access controls and data governance.
Together, RAG and MCP replace scattered code with a single, unified interface for data access, similar to how USB-C replaced many different cables. This combination enables the move toward Agentic AI, where models go beyond simple chat and can perform complex, multi-step tasks with production-ready reliability.
The concepts discussed in this article are based on findings from the scientific papers cited, which readers may refer to for a more comprehensive technical understanding.
- A Comprehensive Survey of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Evolution, Current Landscape and Future Directions (Read Paper)
- Hallucination Mitigation for Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Models (Read Source)
- Reducing hallucination in structured outputs via Retrieval-Augmented Generation (Read Research)
FAQs
Q1. What exactly is an AI hallucination?
Ans. An AI hallucination occurs when a Large Language Model (LLM) generates an output that sounds confident and plausible but is factually incorrect, nonsensical, or irrelevant. In high-stakes legal queries, hallucination rates have been observed as high as 69% to 88%.
Q2. How does Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) stop hallucinations?
Ans. RAG prevents hallucinations by grounding the LLM in real-time, authoritative data retrieved from a company’s own internal sources. Instead of relying solely on its static and often outdated training data, the RAG workflow fetches specific documents or facts relevant to a user’s query and incorporates them into the prompt, ensuring the model’s response is anchored in external evidence.
Q3. What is the Model Context Protocol (MCP)?
Ans. The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open-source, standardized interface developed to connect AI applications to external data sources and tools without custom glue code. It functions as a universal connector that allows models to dynamically discover and use data from various enterprise systems like CRMs, databases, and local files.
Q4. How do RAG and MCP work together to ensure accuracy?
Ans. RAG and MCP are complementary technologies. MCP provides the governed data-access layer (the infrastructure), while RAG is the technique used to retrieve the most relevant context through that layer at query time. MCP standardizes how the AI plugs into data, and RAG ensures that once connected, the AI uses that data to provide grounded, factual responses.
Q5. What is the “Librarian and Security Guard” analogy of MCP?
Ans. This analogy draws a comparison of MCP’s dual role,
- The Librarian: Uses Agentic Retrieval and Context Structuring to find the exact page of information needed, precisely formatting it for the LLM to minimize guesswork.
- The Security Guard: Employs Security Enforcers to check user permissions (RBAC) and mask sensitive data (PII) before it ever reaches the LLM, ensuring regulatory compliance.
Q6. Can RAG itself hallucinate?
Ans. Yes. “RAG hallucinations” can occur if the system relies only on unstructured, noisy data. For instance, a chatbot might retrieve an incorrect bill or a misleading policy because the internal knowledge base itself was flawed or lacked specific context. Advanced “RAG+” or GenAI Data Fusion addresses this by integrating both structured (databases) and unstructured data for higher precision.
Q7. Does implementing RAG and MCP reduce AI infrastructure costs?
Ans. Scientific evidence shows that coupling a smaller, well-trained retriever (e.g., 110M parameters) with a smaller LLM (e.g., 3B or 7B parameters) can match or exceed the performance of massive 15.5B+ parameter models without RAG. This allows for higher system throughput on existing hardware, significantly reducing the total cost of ownership for enterprise AI.
Q8. What are “Response Validators” in the RAG/MCP stack?
Ans. Response Validators (or Guardrails) act as the last line of defense. They intercept the LLM’s output before it reaches the user, scrutinizing it for factuality, compliance, and safety. If a response contradicts the retrieved context or violates an enterprise policy (e.g., “do not disclose account balances”), the system can flag, modify, or block it entirely.
Q9. How does MCP help with regulatory compliance, like GDPR or HIPAA?
Ans. MCP builds security into the protocol level. Its Security Enforcers apply granular access controls, ensuring an AI agent only “sees” data that a specific user is authorized to view. It also uses data masking to hide sensitive values (like health records or financial figures) while allowing the LLM to process the necessary context for the task.
Q10. What metrics are used to measure the success of a RAG system?
Ans. Scientific benchmarking utilizes several “pinpoint” metrics:
- Trigger Exact Match (EM): Verifies if the output matches the ground truth exactly.
- Bag of Steps (BofS): Measures the overlap between generated and expected steps in an order-agnostic way.
- Recall@K: Evaluates if the necessary facts are included within the top retrieved results.
Q11. What is “Agentic AI” in this context?
Ans. Agentic AI refers to sophisticated agents that move beyond simple chatbots to perform complex, multi-step tasks autonomously. By using MCP and RAG, these agents can navigate various data silos, schedule events, or troubleshoot manufacturing errors with a “single source of truth,” moving AI from an experimental tool to production-ready orchestration.
Q12. Why shouldn’t businesses plug AI agents directly into their core systems?
Ans. This “Dangerous Direct Access” approach often gives agents only a partial view of data without understanding business logic or cross-departmental impacts. Without the layered governance and context harmonization provided by MCP, agents are forced to “guess around the gaps,” leading to real-world errors like bad price routing or unauthorized approvals.














